Learn how your business can get the most out of the latest software and technology.
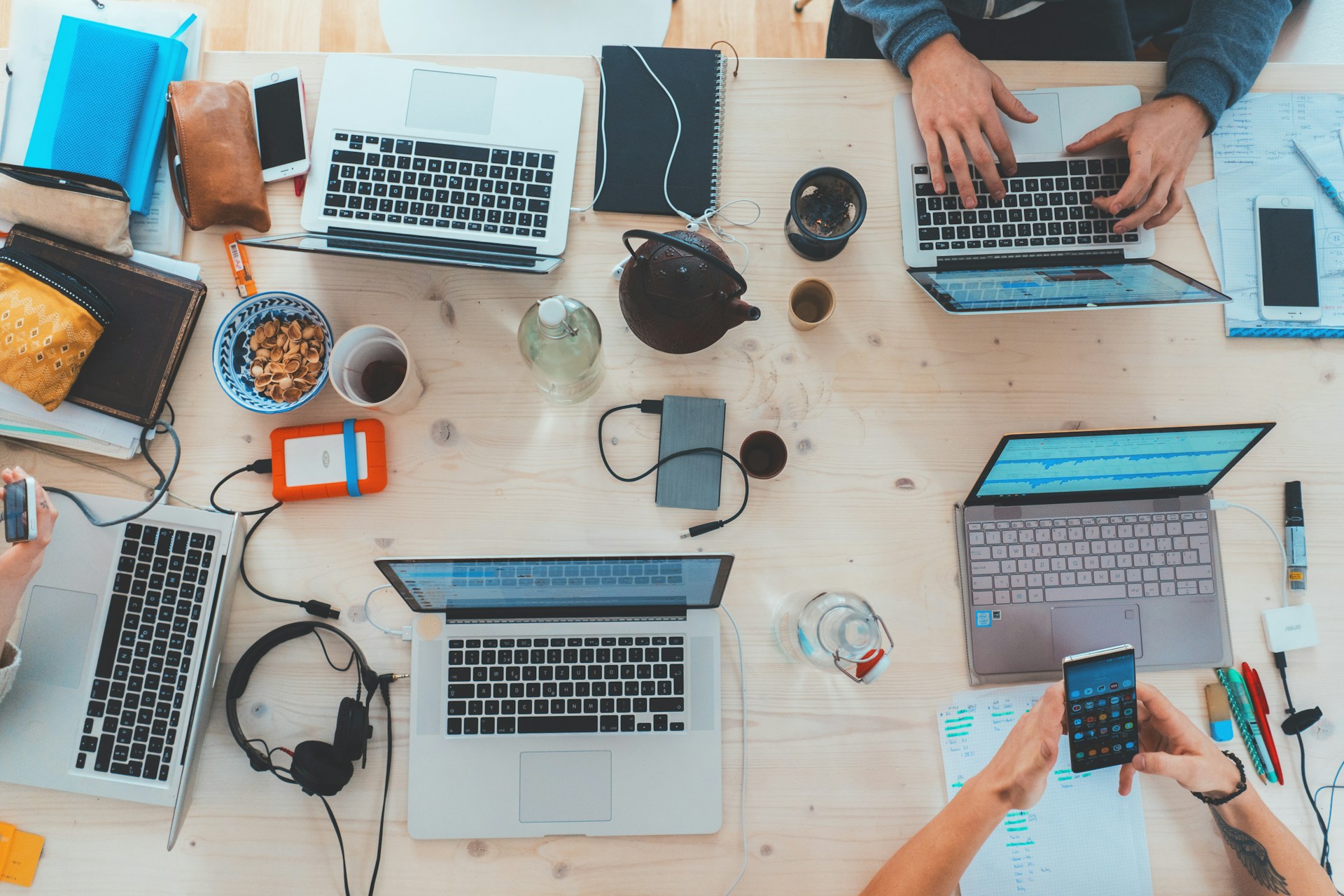
The way we do business now is worlds apart from how business was conducted years ago. While the basic tenets of running a business remain the same, in that you want to maximize profits, reduce costs, and grow your business’s infrastructure and customer base, the methods used are very different.
For example, technology now plays a significantly larger role in businesses than ever before. Once, a small business could run quite comfortably without an internet connection, relying on traditional marketing, word of mouth, and great service to win over loyal customers. But things have changed, largely for the better.
Even small businesses aren’t just recommended to use the internet and other software to further their business; it’s practically a requirement.
The business world has consistently been at the forefront of technological advancements and innovation. If we can utilize something to generate income, it will be developed and utilized for that purpose, and any business that neglects to keep up will be left by the wayside.
So, how can your business benefit the most from software and technology? Here are a few ways it can improve your company.
Table of Contents
Digital Marketing And Social Media
A business can’t grow without its customers, and you’re never going to find customers unless you look for them. Marketing is a valuable tool in a business owner’s arsenal, and you can find many different ways to market your business to different people.
Much like everything else, software and technology play a vital role in ensuring that your marketing strategies are as effective as possible. You’re investing time and money into your marketing, so it makes sense to do whatever you can to help it pay off.
While traditional marketing methods still have their place, especially if you run a local brick-and-mortar business and still rely on people walking past, the future is comfortably in the arms of social media and other digital marketing methods.
Effective marketing relies on brand recognition and exposure, and people must see your brand before they can recognize it. Most people, even older individuals, are often found scrolling through some form of social media. Therefore, it stands to reason that leveraging social media platforms is a surefire way to enhance your marketing success.
Social media marketing is more than just creating an account, posting a few times, and hoping for the best. If it’s going to work, you need to put in the work. Post helpful, interesting content regularly. Plan your social media posts carefully and determine what will be most effective for your target audience. You should also keep an eye on the algorithm and any recent trends, as these can significantly boost your exposure.
Of course, there are other methods of digital marketing, such as email campaigns, content marketing, and advertisements. A good strategy is one that is well-balanced. However, you can also utilize software to assist you in planning these campaigns. For example, AI marketing tools can help you plan and implement a campaign designed to suit your customers, and some tools can even create adverts so you don’t have to.
This cuts out time and increases your chances of success. In the business world, these are both significant victories.
READ ALSO: Important Marketing Tips Every New Business Should Know
Organization and Communication
It’s all very well and good trying to reach as many customers as possible, but if your organization isn’t well-organized, you won’t get any work done. This means that you can’t deliver a good service to your customers, and you won’t be able to be as productive or efficient as you could be.
As we all know, time is money. When time is money, more efficient processes are the only way to ensure that your business remains strong.
So, organizational tools can be your best friend. Communication is essential, especially when working as a team or communicating with clients. Poor communication leads to mistakes, delays, and frustration.
Utilize software and technology where possible to enhance these processes.
By now, we’re more than familiar with the different technologies we can use to communicate with one another. Instant messaging and video conferencing have taken the world by storm, especially with the rise of remote work. Ensure that important conversations are saved so you can refer back to them.
When it comes to experts or technicians who deal with customers in the field, use a field service app to keep track of your technicians and their projects. BuildOps offers a great service that’s easy to use and keeps everything in a logical order.
Even if a tool saves just a few minutes per job, those minutes quickly add up. So, use what you can to shave as much time as possible from your projects. You never know what else you might have time for.
Your customers and employees alike will thank you as well.
READ ALSO: Why Digital Marketing Is Crucial for Startup Success
Cybersecurity
So far, we’ve covered a few of the many ways businesses can use software and technology to change how they operate. But this is a double-edged sword. The more we rely on technology, the more vulnerabilities we open up in our IT systems.
So, how can you balance the need to work efficiently, effectively, and with all the power that software can offer, without opening yourself up to more risk?
This is where cybersecurity comes into the picture. There is a constant arms race between cybersecurity systems and hackers, and it’s vital to keep on the cutting edge of security. If the wrong person gains access to your systems, they can cause significant damage.
So, train your employees to spot potential threats and suspicious emails. Plan how to keep your business secure and always research both the methods hackers are using and how you can prevent them. This way, you can get the best of both worlds. You have the power of technology while mitigating the risk.
INTERESTING POSTS
- The Ultimate Social Media Security Guide for Individuals and Businesses
- Take Your Small Business To The Next Level With YouTube Marketing
- How To Start A Cybersecurity Company
- 3 Critical Cybersecurity Questions To Ask Before Buying a Marketing SAAS Product
- 4 Essential Tactics For Increasing Sales Today
- Website Security Check: How Secure Is Your Website?
- A Look at New Forms of Marketing and How to Implement Them