This post will discuss cloud security, its components, and cloud security framework models provided at various service levels. Also, we will show you why companies should move their businesses to the cloud. Cloud computing is highly popular and widely adopted by almost every possible domain.
And it is expected to reach 623.3 Billion by 2023. But still, whenever it comes to migrating your business to the cloud, several concerns pop up.
As per the survey conducted by Statista in the first quarter of 2020, 83% of technical executives, managers, and cloud practitioners from around the world expressed that cloud security is a crucial challenge for them.
Gartner reports stated that around 38% of companies fear moving to the cloud due to security and privacy concerns. Let’s start this by understanding Cloud Security.
Table of Contents
What Is Cloud Security?
Cloud security is a set of policies and procedures that protect data on the remote servers from data corruption, theft, leakage or data loss. Security measures protect cloud data and customers’ privacy by setting individual authentication rules.
In cloud security, it is crucial to highlight the significance of eDiscovery. As businesses transition to the cloud, they must also consider legal and compliance requirements related to electronic discovery (eDiscovery).
eDiscovery involves identifying, preserving, and producing electronically stored information (ESI) for legal cases or investigations. Incorporating eDiscovery capabilities into your cloud security strategy ensures that you can effectively manage and retrieve relevant data when required, thus meeting legal obligations.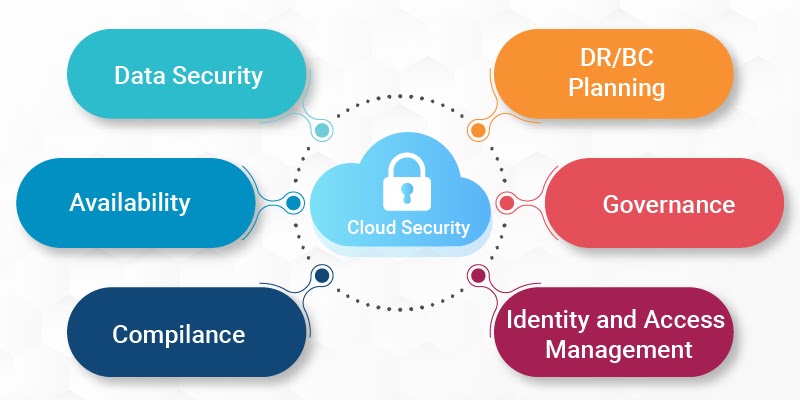 These are the following components that come under cloud security and protection:
These are the following components that come under cloud security and protection:
Data Security
Several data threats are associated with cloud data services, including Denial of service attacks, side-channel attacks, Data breaches, insider threats, Malware injection, Insecure APIs, virtualisation threats, and Abuse of Cloud services. Data security ensures protection from these vulnerabilities.
Availability
This expresses the context of data and services available. And that will be transmitted to your location encrypted and secured.
Compliance
Cloud compliance specifies the laws and regulations that apply while working. It also includes access to information laws which may enable governance.
DR/BC Planning
Cloud Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity refers to the planning of technologies and services that can be applied during mishappening or unplanned events with minimum delay in Business.
Governance
Cloud security governance is a management model that conducts security management and operations in the cloud to ease business targets. It explains the methodology of structures, operational practices, performance expectations and metrics for optimising business value.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
This covers products, processes and policies (3Ps). Companies use the set of 3Ps to manage user identities within an organisation. Also, it is used to validate user access. These components are protected by cloud security.
Cloud Security Framework Provided At Different Service Models
With last year’s rate of cloud threats, it’s essential to ensure its security at multiple levels. So here we’ll let you know about cloud security frameworks at a different level of service models.
Firewall Security
A firewall provides an increased security configuration to the cloud architecture. Cloud Firewall is built to stop or barricade unwanted access to private networks. The idea is to limit the form of available open ports.
A few ports are assigned for various services, such as web server groups that open port 80 (HTTP port) and 443 (HTTPS port) to the world. But for application servers only open port 8000 (different application service port) for web server group, Database server group only open port 3306 (My SQL port) for the application server group.
Also, simultaneously, the three other groups of network servers open port 22 (SSH port) for customers and, by default, refuse other network connections. This process of creating specified ports will improve security.
Security action of SaaS
SaaS, i.e., software as a service, provides capability and accessibility to the customer for using the provider’s applications running on the cloud. Here, the basic end-user will try to secure their data and access.
The security function here has two main aspects: Priority Access Control Strategy: SaaS providers offer identity authentication and access control functions. To eliminate the possibilities of security threat of the cloud applications internal factors.
Simultaneously, cloud providers should ensure the high strength, change password at a period, make password lengthy and sensitive and should not use the function such as an old password to increase the security of a user account.
Common Network Attack Preventions: As a defensive measure of protection against network attacks such as DDOS attacks, providers use several methods like configuring a firewall, blocking the ICMP or any unknown protocol. And eliminate and shut down unnecessary TCP/IP services.
Providers can also monitor the TCP service regularly and update software patches at a time. Along with these broadly assigned security functions, other prevention mechanisms include Detecting rogue services and compromised accounts, applying Identity and Access Management (IAM), Encrypt Cloud Data, enforcing Data Loss Prevention (DLP) and monitoring collaborative sharing of data.
Security action of PaaS
PaaS, i.e., Platform as a Service, provides a platform for the client to develop, run, and manage the applications. Not to mention, the end-user is responsible for securing their user access, data, and applications.
PaaS is the middle layer, and there are two aspects of security measures. The first is the virtual machine technology application, which provides providers with virtual machines in existing operating systems for the customers. With extending OS permissions, set access restrictions for users’ operations.
SSL attack Defending: Cloud providers should give corresponding patches and measures. Simultaneously, using the firewall to close some port to prevent frequent attacks and strengthen management authority.
Along with these two aspects, there is a Cloud access security broker (CASB), Cloud Workload Protection platforms (CWPP) and cloud security posture management (CSPM).
Security action of IaaS
IaaS, i.e., Infrastructure as a Service, provides virtualized computing resources via the Internet. Here, the user will secure their applications, OS, data, user access, and virtual network traffic.
It’s generally not directly in touch with users. Its maintenance and management rely on the provider. Cloud providers should provide information on the actual servers’ location, and operating data shouldn’t be a problem. Ensure the security of different user data, along with encryption.
There’s a need to separate user data stored in different data servers. Also requires data backup of essential and confidential data so reduce recovery time from any uncalled disaster.
Also, there are other security norms for IaaS, such as Cloud Security Gateway (CSG), Virtual Network security platforms (VNSP), Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) and Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP).
Why Should Companies Choose To Move Their Businesses On The Cloud?
 There’s no denying the increasing rate of data breaches and other vulnerabilities, but we shouldn’t ignore the precautions and protection mechanisms we are implementing. With continued advances in emerging technologies, cloud providers will also develop new protection management systems.
There’s no denying the increasing rate of data breaches and other vulnerabilities, but we shouldn’t ignore the precautions and protection mechanisms we are implementing. With continued advances in emerging technologies, cloud providers will also develop new protection management systems.
If you decide to move to the cloud, take records and stock of sensitive information and ensure you understand and trust the cloud provider and its services to protect your data. Choose a provider that identifies security as its primary concern, even during cloud migration. Look for the performance and their data protection solutions.
Check for the load balancing and traffic handling techniques. Don’t fall for the myth of losing control; you will have control and access to the resources.
Bottom Line
With the merge of IoT and Cloud Computing, we are making progress in protecting your data against threats. Cloud providers take care of their customers’ problems. There are 24/7/365 days of free IT customer support and easy access to cloud experts for your business development. You don’t need to worry about teaching your staff and hiring several IT professionals to handle your cloud system.
Cloud hosting isn’t as expensive as you assume. Choose a cost-efficient and reliable provider for your business. The cloud industry is setting its roots in all domains. The flexibility, scalability, reliability and productivity are the reasons behind the success of the cloud computing industry. Business owners generally choose the cloud as a service to avoid facing unpredictable trade wars and geopolitical changes.
Now, clients are even more inclined to implement new technologies in their work. If you still haven’t gained much confidence in deploying your business over the cloud, start small with few data records and then scale it up further.
Cloud computing is the trend, and cloud security will always be critical. Nothing is 100% secure, and it’s a universal truth. So, opt for something with the maximum protection possible.
Note: This was initially published in August 2020, but has been updated for freshness and accuracy.
RELATED POSTS
- 9 Proven Cybersecurity Tips For Startups
- Network Firewalls: Comprehensive Guide For Non-Tech-Savvy People
- Breachers Gonna Breach: Protect Your Organization From Internal Threats
- Complete DeleteMe Review [100% WORKING]
- How To Keep Your Cloud Storage Safe And Secure
- Take Your Small Business To The Next Level With YouTube Marketing
- Multi-Platform Malware Framework ‘MATA’ On A Global Rampage
- What Next After Being Scammed Online?
- Best Cloud Storage Services According To Reddit Users
About the Author:
Amaya Paucek is a professional with an MBA and practical experience in SEO and digital marketing. She is based in Philippines and specializes in helping businesses achieve their goals using her digital marketing skills. She is a keen observer of the ever-evolving digital landscape and looks forward to making a mark in the digital space.
Christian Schmitz is a professional journalist and editor at SecureBlitz.com. He has a keen eye for the ever-changing cybersecurity industry and is passionate about spreading awareness of the industry's latest trends. Before joining SecureBlitz, Christian worked as a journalist for a local community newspaper in Nuremberg. Through his years of experience, Christian has developed a sharp eye for detail, an acute understanding of the cybersecurity industry, and an unwavering commitment to delivering accurate and up-to-date information.






